Music industry revenues in review – what 2022 tells us about 2023

With a 2023 set to be a challenging year for the global economy, it is a good time to look at how the music industry has performed in the year to date. That is exactly what we have done in our forthcoming report: ‘Music industry earnings Q3 2022: Pre-recession growth’. We have tracked the performance of leading labels, publishers, DSPs, and live companies across the globe to create a holistic view of how the music business is performing across rights, distribution and live. Here are a few highlights that provide useful pointers as to how 2023 might shape up.
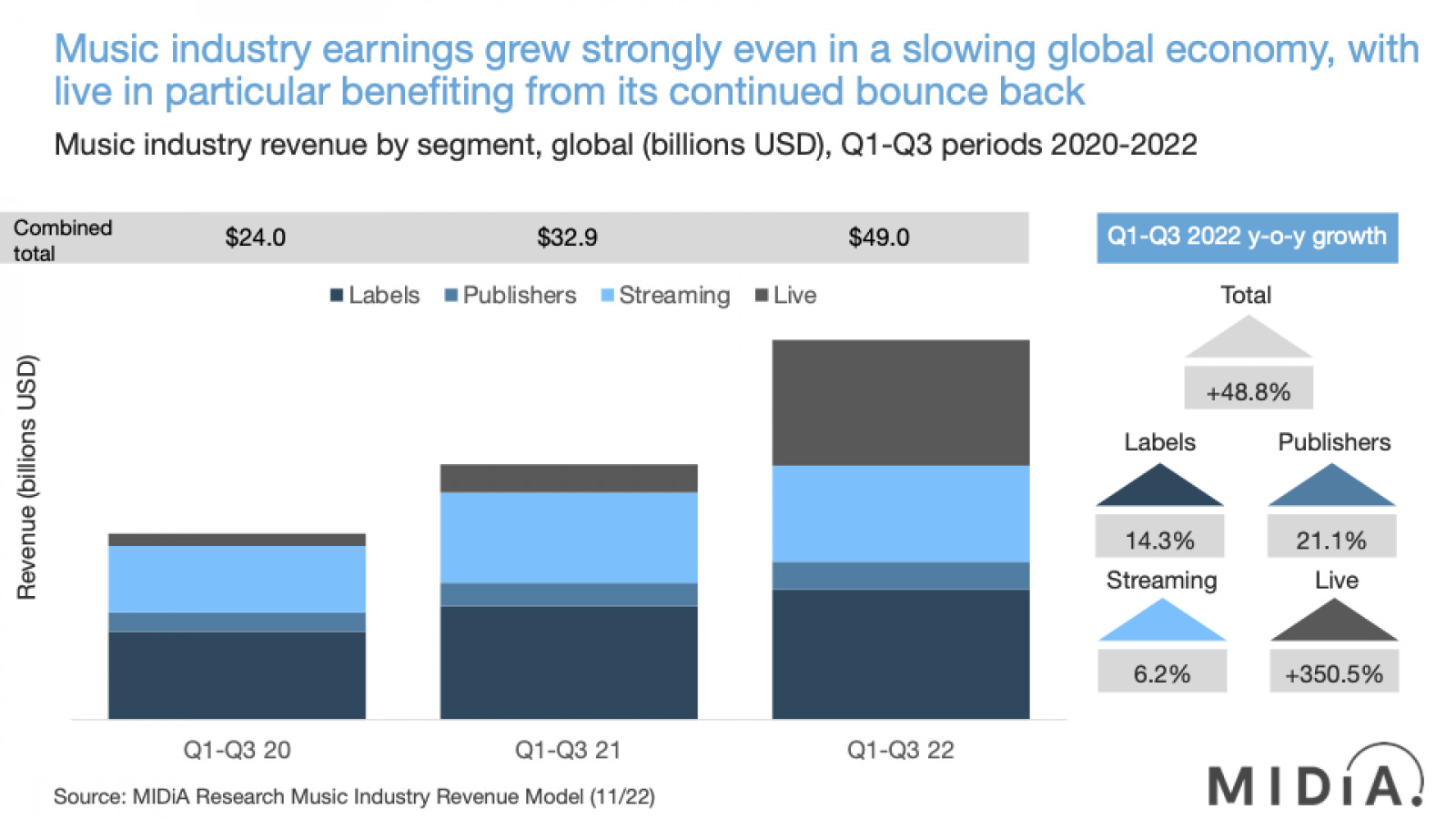
These are the key trends for revenue growth for Q1-Q3 2022 compared to Q1-Q3 2021:
· Record labels were up 14.3%, which is above the 11.8% that MIDiA forecasted at the start of the year, but with Q4 looking to be the quarter most heavily hit by the economic downturn, the full-year figure may well end up closer to 12% than 14%. Nonetheless, double-digit growth is commendable performance in such a tough economic environment, and bodes well for 2023.
· Publishers were up 21.1%, outperforming labels, reflecting factors such as the effect of historical digital royalty settlements, improved shares of streaming revenue (especially non-DSP), and the rebound of traditional performance income. Publishers have worked hard over recent years to ensure that they get a large share of income flowing to their songwriters, and 2022 reflects a job well done, though, of course, with further room for improvement.
· DSPs saw revenue growth of a more modest 6.2%, though this was pulled down by a dramatic slowdown in the Chinese market with Tencent Music Entertainment’s revenues flat. Spotify performed more strongly (7.7%), which was almost exactly in line with the major label’s streaming revenue growth of 7.3%. Subscriber growth across all companies was more than ten points stronger, thus indicating that consumer demand for streaming is strong going into 2023.
Featured Report
Splice x MIDiA Sounds of 2026 House on the rise
We zoom in on the trends and microtrends driven by the music industry’s biggest fans and most influential tastemakers: creators. Turn page after page of trends unfolding in real-time and see how Splice’s dataset is the barometer for the state of music today.
Find out more…· Live continued its post-Covid rebound, with dramatic growth, benefiting from the still strong latent demand both from consumers and artists, eager to get touring again. However, with going out and going to concerts being the main things that consumers state they will cut back on during the recession, live may find the coming year more difficult than music rightsholders and DSPs.
Recessions have a habit of being self-fulfilling prophesies, with companies slowing down spend in anticipation of a coming slowdown, thus slowing down revenue growth for their suppliers, who then pass on the same cut backs to their suppliers and so forth. Despite all this, music rights and streaming may be well placed in the recession.
The lipstick effect
The case for music lies in lipstick, of all places. During previous recessions, lipstick sales boomed, representing an affordable luxury for consumers who could no longer afford the big-ticket items that they had been saving for or were used to buying. Music subscriptions may play an affordable luxury role, the soundtrack to evenings spent at home, when going out is a cost too far.
The early 2020s saw an influx of capital into the music business, with the promise of music rights being an asset class that was uncorrelated with the wider economy. The irony is that, as music catalogue investments slowed (due to rising costs of capital), the first nine months of 2022 saw the music business deliver a performance that suggests the industry is indeed setting a path that is not being pulled down by recessionary conditions as much as many other industries. There were areas of concern, of course, but the overall picture so far is a positive one.

The discussion around this post has not yet got started, be the first to add an opinion.